Javascript, the DOM & You.

Hello again friend :)
Intro.
Today we explore Javascript and it's relationship to HTML & CSS.
We will explain what
Control Flow & Loops are.
Give you a description of the DOM and an interaction example.
Explain differences between arrays & objects and how getting data from each differs.
We will end this exploration with an explanation on Functions.
Javascript. HTML. CSS.
Think about any movie you have ever seen.
HTML would be stripping everything to its basics of what you see on screen,
whats left are actors appearing on a screen.
CSS adds in the detail, the clothes, color, props and set.
CSS makes things pretty.
Finally you have JavaSCRIPT, very aptly named.
It is the controlling aspect of what you see onscreen,
what the actors say, what you hear, the interactions with everything.
In the end they all combine to create something magical.
Control Flow. Loops.
Control flow is how your computer reads and runs your code.
Like how you would read a numbered checklist. 1, 2, 3, 4, etc...
this would be how it
flows
The control part is any statement that changes the flow for example:
This (very badly drawn image I did in paint.) is the basic concept of a looping statement.
What are Loops?
Well my friend Loops are a simply a statement
that keeps running again and again
until there is nothing left to loop or the condition becomes false.
If we take the above image as an example. Say your making sandwiches for your family or friends.
The loop would be making the sandwiches, the condition to stop would be nobody else wants anymore sandwiches.
And thus the loop is broken and you get to have lunch with the people you made food for.
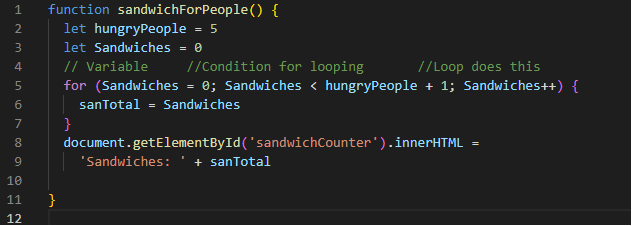
This code shows how a loop would work if you were to use it to make sandwiches and you had 5 hungry people
Please Ignore the + 1 in the conditional as Javascript starts counting from 0
in most cases so we have to account for that(Just imagine one sandwich flew off into the void).
The DOM.
This section will not include whips, paddles or the Torreto Familiy flying cars into outer space(unfortunately).
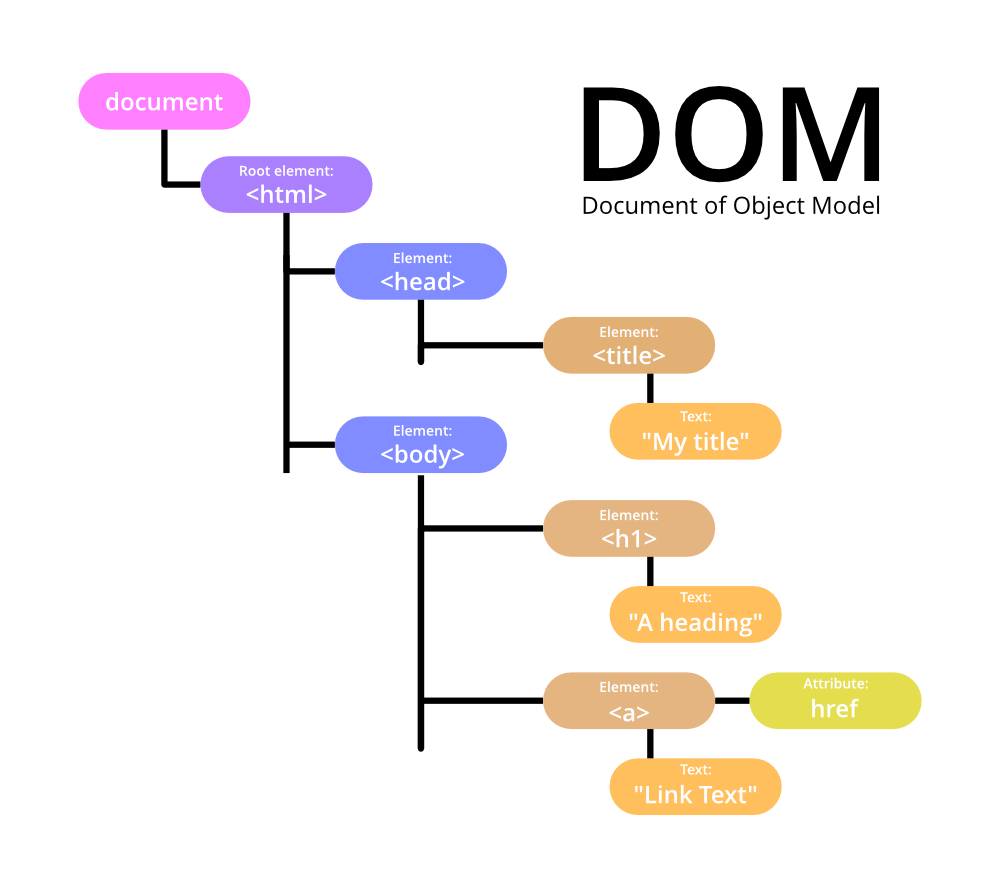
The DOM we are referring to today is the Document Object Model.
This neutral interface that allows programs and scripts to
change the structure and style of a document.
This is the structure that the DOM represents as little nodes and objects.
We can imagine this as clay. HTML, JavaScript and CSS would be the artist molding the clay
how it sees fit to create a magical web page.
Interaction Example
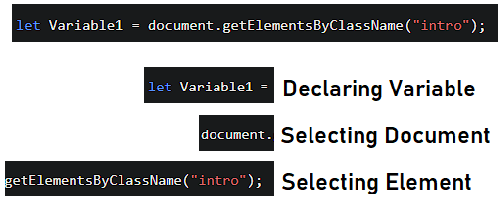
This line of code is written in JavaScript.
breaking it down like this lets you see how the DOM is able to be selected by objects, classes and IDs.
Using this you could manipulate the element where this class is located.
Objects{} vs. Arrays[]
Objects and arrays are ways to store data in javascript.
But the way they are stored is different.
Arrays use an index to store information. for example:
let coffee = [Latte, FlatWhite, Black, Espresso, Irish]
because JavaScript starts counting in arrays at 0, Latte here would be called as
coffee[0]. Irish being coffee[4]. Arrays are accessed using the number equivalent from the array using the specified index number.
Objects store data using //Key: "Value"// pairs. The key would be a folder/binder you had and the value would be the data stored within.
For Example:
let cake = {
flavour: "chocolate",
icing: "vanilla buttercream",
shape: "square"
type: "brithday"
}
This is the data stored within the Object Cake.
Using the object.key we can get the code to tell us that cake.flavour is "chocolate".
Using the object['Key'] would get the same result using differnt syntax.
Functions
Functions are a set of statements that performs a task or calculates a value. They are not used unless called upon.
Sound confusing? Well lets now imagine you are a coach for a sports team. Every function is a set play that you get your team to execute.
But the team doesnt know to execute it unless you tell them to.
In Javascript, you can use these at anytime anywhere.
Functions are always ready.